Description
Given a polyline defined by an ordered list of 2D coordinates, return a list of n equidistant coordinates on that polyline.
Sample input:
coords = [
(-4, 1), (-1, 1), ( 0, 4),
( 1, 1), ( 4, 1), ( 2, -1),
( 3, -4), ( 0, -2), (-3, -4),
(-2, -1), (-4, 1)
]
Solution
import math
def point_dist(p1, p2):
"""Distance between two points"""
return math.sqrt((p2[0] - p1[0]) ** 2 + (p2[1] - p1[1]) ** 2)
def p3_along_p1_p2(p1, p2, dist):
"""Returns (x, y) point at a given distance from p1 and along the
line created by p1 and p2
"""
dist_btw = point_dist(p1, p2)
dist_ratio = dist / dist_btw
x = (1 - dist_ratio) * p1[0] + dist_ratio * p2[0]
y = (1 - dist_ratio) * p1[1] + dist_ratio * p2[1]
return x, y
def point_seq_length(coords):
"""Compute distance of sequential (x, y) list along a route"""
return sum([point_dist(p1, p2) for p1, p2 in zip(coords, coords[1:])])
def equidist_pts_on_line(coords, n_pts):
"""Equidistant points along route
coords: sequential (x, y) list along a route
returns: (eq_coords, segment_len)
"""
route_len = point_seq_length(coords)
segment_len = route_len / (n_pts - 1)
segment_len_remain = segment_len
curr_p = coords[0]
eq_coords = [coords[0], ] # add the same first coordinate
next_coord_idx = 1
while True:
next_p = coords[next_coord_idx]
dist_to_next = point_dist(curr_p, next_p)
if segment_len_remain > dist_to_next:
segment_len_remain -= dist_to_next
curr_p = next_p
next_coord_idx += 1
else: # segment_len_remain <= dist_to_next
# place an eq_coord segment_len_remain distance from curr_p
# on the line created by curr_p and next_p
eq_coord = p3_along_p1_p2(curr_p, next_p, segment_len_remain)
eq_coords.append(eq_coord)
curr_p = eq_coord # update curr_p to our new point
if len(eq_coords) == n_pts: # solve condition
break
# do not update next_coord_idx
# recompute these to reduce accumulated error
route_len = point_seq_length([curr_p] + coords[next_coord_idx:])
segment_len = route_len / (n_pts - len(eq_coords))
segment_len_remain = segment_len
return eq_coords
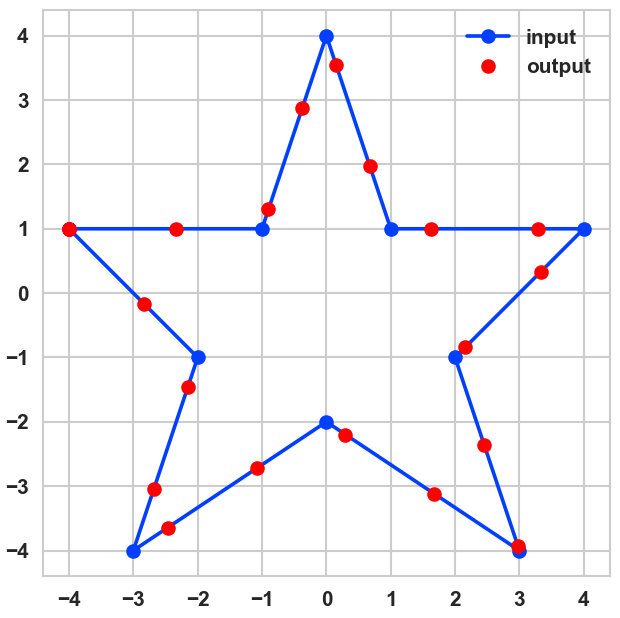
Plot our solution with:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use('seaborn-whitegrid')
coords = [
(-4, 1), (-1, 1), ( 0, 4),
( 1, 1), ( 4, 1), ( 2, -1),
( 3, -4), ( 0, -2), (-3, -4),
(-2, -1), (-4, 1)
]
eq_coords = equidist_pts_on_line(coords, 20)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))
ax.plot([p[0] for p in coords], [p[1] for p in coords], 'o-',
label='input')
ax.plot([p[0] for p in eq_coords], [p[1] for p in eq_coords], 'o',
color='red', label='output')
ax.legend()
ax.set_aspect('equal')
fig.savefig('Basic.png', dpi=150, facecolor='white');